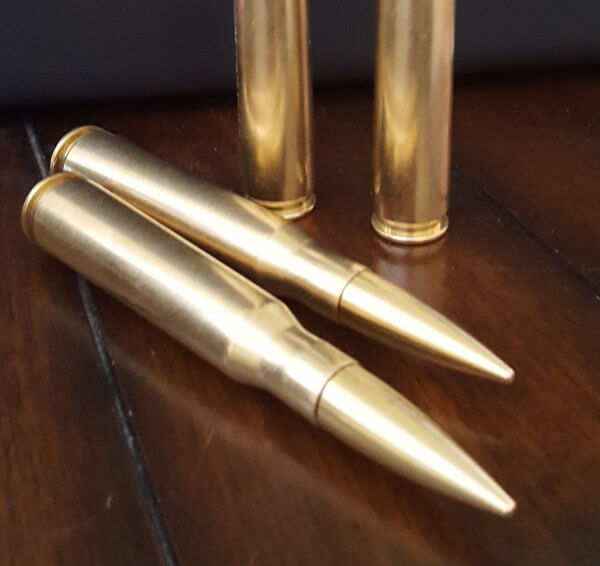
The .50 Browning Machine Gun (.50 BMG, 12.7×99mm NATO and designated as the 50 Browning by the C.I.P) is a .50 in (12.7 mm) caliber firearm cartridge developed for the M2 Browning machine gun in the late 1910s, entering official service in 1921. Under STANAG 4383, it is a standard service cartridge for NATO forces as well as many non-NATO countries. The cartridge itself has been made in many variants: multiple generations of regular ball, tracer, armor-piercing (AP), incendiary, and saboted sub-caliber rounds. The rounds intended for machine guns are made into a continuous belt using metallic links.
The .50 BMG cartridge is also used in long-range sniper rifles and anti-materiel rifles. A wide variety of ammunition is available, and the availability of match grade ammunition has increased the usefulness of .50 caliber rifles by allowing more accurate fire than lower quality rounds.
إن مدفع رشاش براوننج .50 (.50 BMG ، 12.7 × 99 ملم من الناتو والمسمى بـ 50 Browning بواسطة CIP) عبارة عن خرطوشة سلاح ناري من عيار 0.50 بوصة (12.7 ملم) تم تطويرها لمدفع رشاش براوننج M2 في أواخر عام 1910 ، الخدمة الرسمية في عام 1921. بموجب STANAG 4383 ، تعد خرطوشة خدمة قياسية لقوات الناتو وكذلك العديد من الدول غير الأعضاء في الناتو. تم تصنيع الخرطوشة نفسها في العديد من المتغيرات: أجيال متعددة من طلقات الكرة العادية ، والمتتبع ، وخارقة للدروع (AP) ، والحارقة ، والمخربة. تصنع الطلقات المخصصة للرشاشات في حزام متواصل باستخدام روابط معدنية. تُستخدم خرطوشة .50 BMG أيضًا في بنادق القنص بعيدة المدى والبنادق المضادة للعتاد. تتوفر مجموعة متنوعة من الذخيرة ، وقد أدى توفر ذخيرة من الدرجة المطابقة إلى زيادة فائدة بنادق عيار .50 من خلال السماح بإطلاق نار أكثر دقة من الجولات الأقل جودة.